This article provides a complete, experience-based overview of shipping from Vietnam to USA, including transportation methods, cost structure, transit time, major ports, shipping routes, and how Dantful International Logistics
Overview of Shipping from Vietnam to USA
Vietnam is one of the fastest-growing manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia, supplying the US market with furniture, garments, electronics, home goods, and consumer products.
From our daily operations on the Vietnam–USA trade lane, we see that most shipping issues are not caused by ocean transit itself, but by:
- Incorrect cost expectations
- Incomplete documentation
- Poor port or route selection
- Lack of coordination between export and import processes
Choosing the right shipping strategy early helps importers control total landed cost, reduce delays, and avoid unnecessary risk.
Selecting the appropriate shipping method depends on cargo volume, urgency, and budget tolerance.
Sea freight remains the most cost-effective option for bulk shipments.
-
FCL (Full Container Load) Suitable for large volumes requiring a dedicated container, offering better cost efficiency per unit.
-
LCL (Less than Container Load) Designed for smaller shipments sharing container space, charged based on volume (CBM).
Best suited for: Non-urgent cargo, stable supply chains, cost-sensitive shipments.
From our experience, LCL shipments are more sensitive to consolidation schedules than sailing dates, which should be considered when planning timelines.
Air Freight from Vietnam to USA
Air freight offers significantly faster transit at a higher cost.
-
Charged by chargeable weight (actual vs volumetric weight)
-
Requires accurate packing and documentation
Best suited for: Time-sensitive, high-value, or seasonal cargo.
Express Shipping
Express courier services are available for small parcels and documents.
Best suited for:
Shipping costs are dynamic and influenced by seasonal demand, fuel prices, and capacity availability. Below is an estimated cost range for January 2026, a period typically characterized by high demand before the Lunar New Year holidays.
Estimated Shipping Rates (January 2026)
| Shipping Mode | Destination | Estimated Cost Range | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCL 20′ Container | US West Coast (LA/LB) | $1,800 – $2,500 | Pre-Tet Holiday Rush, GRI (General Rate Increases) |
| FCL 40′ Container | US West Coast (LA/LB) | $2,200 – $3,200 | High demand for space, possible rolling of cargo |
| FCL 20′ Container | US East Coast (NY/NJ) | $2,800 – $3,800 | Panama Canal restrictions (if applicable), fuel surcharges |
| FCL 40′ Container | US East Coast (NY/NJ) | $3,500 – $4,800 | Longer transit time, higher base freight |
| LCL (Sea Freight) | All Major Ports | $45 – $85 per CBM | Minimum 1 CBM charge usually applies |
| Air Freight | Major Airports | $4.50 – $7.50 per kg | Varies by airline density & urgency (Standard vs Express) |
Note: These rates are estimates for general cargo and do not include local charges (THC, doc fees), customs duties, or insurance. Rates for January 2026 may fluctuate weekly due to the “pre-Chinese New Year” shipping peak.
How to Determine if Your Freight Rate is Reasonable
Receiving a quote is one thing; knowing if it’s fair is another. Here is how to judge:
-
Compare “Apples to Apples”: Ensure the Incoterms are the same. A cheaper CIF quote (to the port only) often ends up more expensive than a DDP quote (to your door) once US local charges are added.
-
Check Validity Date: In volatile months like January, quotes may only be valid for 7-14 days. An expired low rate is not a valid benchmark.
-
Analyze the Breakdown: A reasonable quote should clearly separate ocean freight, local handling charges (Origin/Destination), and fees. If it’s a lump sum, ask for a breakdown to uncover hidden costs.
-
Service Level vs. Price
Transit time varies by shipping method, route, and port selection.
-
Direct sailing vs transshipment
-
Port congestion during peak seasons
-
Weather conditions
-
Customs inspection and clearance timelines
Accurate transit planning helps avoid demurrage, storage fees, and supply chain disruptions
Port selection plays a critical role in cost efficiency, transit reliability, and inland delivery planning.
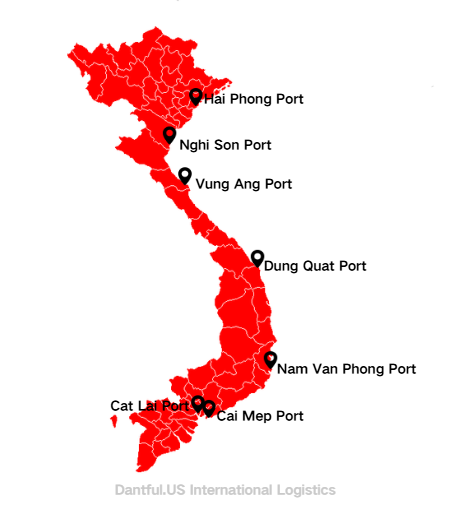
Cat Lai is the largest container port in Vietnam and the primary gateway for exports to the United States.
-
Serves southern Vietnam’s major manufacturing zones
-
Frequent carrier services and strong FCL/LCL capacity
-
Suitable for most export cargo types
During peak seasons, congestion can occur, making early booking and accurate documentation especially important.
Hai Phong Port
Hai Phong is the main port for northern Vietnam, supporting exporters around Hanoi and nearby industrial parks.
-
Strategic for northern supply chains
-
Often used for US West Coast shipments
-
May involve longer routing depending on service availability
Da Nang Port
Da Nang supports central Vietnam exporters.
-
Lower congestion compared to major ports
-
Limited direct services
-
Commonly routed via transshipment hubs
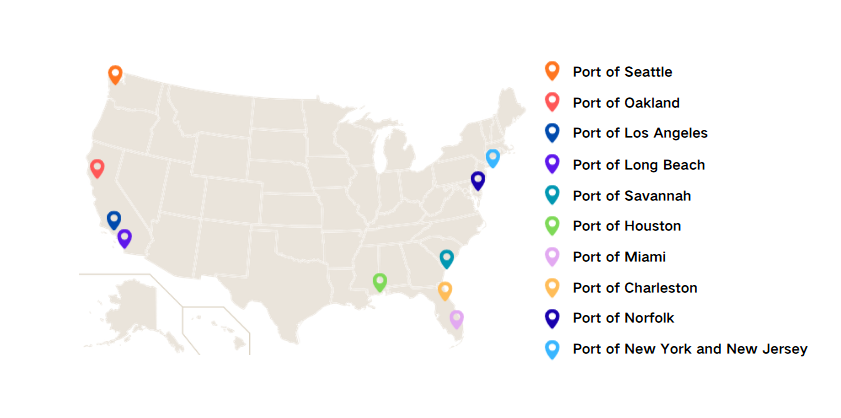
The LA–Long Beach port complex is the most commonly used entry point for Vietnam–USA ocean freight.
-
Shorter ocean transit time
-
Strong rail and trucking connectivity
-
Ideal for Midwest and West Coast distribution
New York / New Jersey
The primary gateway for East Coast deliveries.
-
Longer ocean transit
-
Reduced inland transportation for Eastern US destinations
Savannah
A rapidly growing logistics hub.
-
Efficient port operations
-
Popular for furniture and retail imports
-
Strong access to the Southeastern US
Houston
A key gateway for the Southern and Central US.
-
Strategic for industrial and project cargo
-
Regional distribution advantages
Typical Shipping Routes
Vietnam–USA shipments typically cross the Pacific via:
-
Direct services (faster, limited availability)
-
One-stop transshipment services (more flexible, slightly longer transit)
Route selection should balance cost, reliability, and delivery urgency
All cargo entering the United States must comply with US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) requirements.
Key considerations include:
-
Accurate commercial invoice and packing list
-
Correct HS code classification
-
ISF filing for ocean freight
-
Applicable duties and taxes
While customs inspections are beyond the control of any logistics provider, proper documentation is the most effective way to reduce risk.
What Dantful Can Help?
At Dantful International Logistics, our role is not just to transport cargo, but to help importers control cost, manage risk, and simplify complex logistics processes.
We Support You With:
-
Shipping Strategy Planning Selecting the right transport mode based on cost, time, and cargo profile.
-
Transparent Cost Breakdown Clear explanation of included and excluded charges to prevent surprises.
-
Export & Import Coordination Handling export clearance in Vietnam and import compliance in the USA.
-
Door-to-Door Solutions Integrated ocean or air freight with inland trucking or rail delivery.
-
Risk Management & Communication Proactive updates, issue prevention, and problem resolution throughout the shipment lifecycle.
1. How long does it take to ship from Vietnam to the USA?
Sea freight typically takes 20 to 35 days depending on the port (West Coast is faster than East Coast). Air freight usually takes 3 to 7 days, while Express shipping takes 2 to 5 days.
2. What is the cheapest way to ship from Vietnam to the USA?
For shipments over 100kg or 1 CBM, Sea Freight (LCL) is usually the most economical. For large shipments (over 15 CBM), FCL offers the best value. For small parcels under 100kg, Air Freight or Express might be competitive due to lower minimum charges.
3. How much is import duty from Vietnam to USA?
Import duty rates vary significantly based on the product’s HS Code. Since Vietnam has Normal Trade Relations (NTR) with the US, many items enjoy low tariffs, but specific goods (like textiles or footwear) may have higher rates. Additionally, importers must pay the Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF) and Harbor Maintenance Fee (HMF) for ocean shipments. We recommend consulting Dantful for a precise duty calculation.
4. How long does FedEx take to deliver from Vietnam?
FedEx delivery times depend on the service level chosen. FedEx International Priority typically takes 2 to 4 business days, while FedEx International Economy usually takes 4 to 6 business days. Delays can occur due to customs clearance or remote area deliveries.
5. Why do shipping rates change in January?
January is often a peak shipping month because importers rush to move goods before factories close for the Vietnamese Lunar New Year (Tet Holiday). This increased demand often leads to higher rates (GRI) and tighter space availability.
Request a Shipping Cost Breakdown
Instead of requesting a simple quote, receive a shipping plan with a clear cost structure tailored to your cargo, timeline, and delivery requirements.
Contact Dantful International Logistics
Request
A Free Shipping Quote
Get a fast, free shipping quote from Dantful.US Logistics — your reliable partner for cost-effective, hassle-free global delivery.

